Sprint Historical Velocity¶
(Metric) for Tier: Sprint
Organizational Goal¶
Velocity: Ensure past trends of velocity planning of story points per sprint are taken into account when planning future sprint of work.
Quantitative Goal¶
The ideal trend within 20% of historical data.
Visual Display of Measure¶
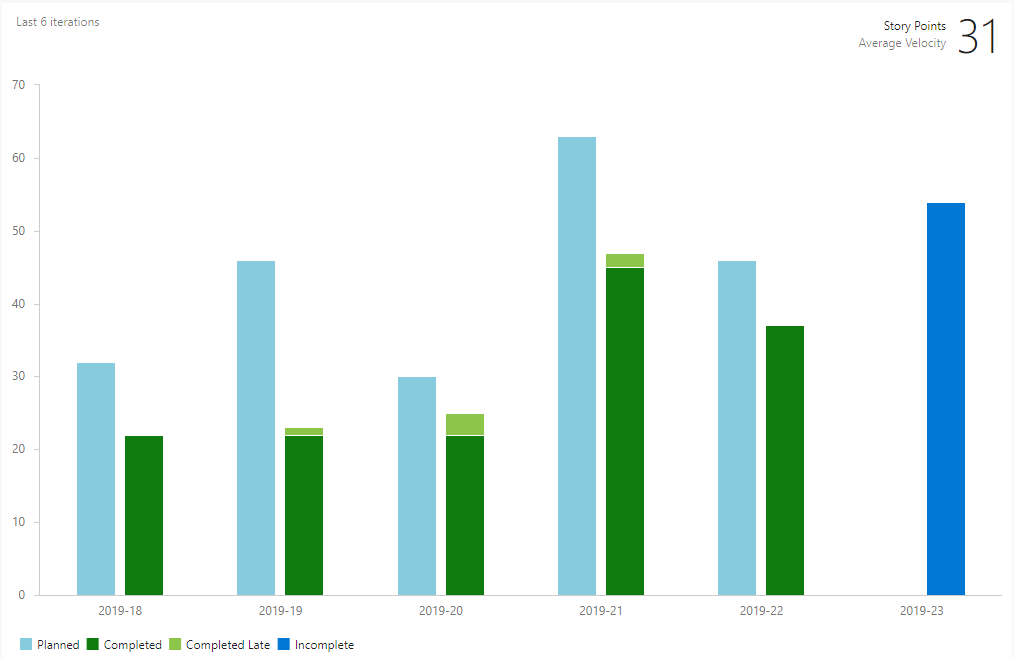
Metric Description¶
Sprint Historical Velocity displays the average velocity in story points of work items assigned to a configured sprint along with a historical trend of story points planned for a sprint against the sum of completed, completed late, and incomplete story points for the last six or more sprints. Reference information in the SEE ALSO section to customize how work items are considered late or planned.
Collection Method, Frequency and Storage¶
The Scrum Master is responsible for ensuring that the Development Team correctly maintains work items in Azure DevOps for the sprint. Work Items need to be assigned to the sprint, have story point values, and be properly closed for Azure DevOps to display this metric. Work items that are assigned to the sprint and their story point value are used to calculate the sum of story points for the sprint. The Development Team configures the start and end time of the sprint to determine sprint length. Azure DevOps calculates an average from six or more sprints allowing a comparison of a given sprint’s velocity with previous sprint performance.
Data Integrity¶
The Development Team configures the sprint during sprint planning with the start and end dates. This allows Azure DevOps to calculate whether work has been completed on time and not. The planned story points are set during sprint planning by assigning User Stories and bugs with story point values to the sprint. User Stories and Bugs are closed during the verify user stories and bugs activity. This closure action indicates to Azure DevOps that the story point in the User Story or Bug is complete and the date is compared to the configured sprint end dates to determine if they were on completed on time or late. The Sprint Review is where non-validated bugs and user stories are returned or removed for the backlog. This action allows Azure DevOps to determine if stories and bugs will be completed late or not completed at all.
Analysis Method¶
- Review if the planned story points are higher or lower than the average story points for the planned sprint. This might indicate that the team is committing to more work than it can complete in the sprint, that the story points aren’t an accurate reflection of sprint work and need to be re-estimated, or the team is running out of work that can be committed to a sprint.
In Conduct Sprint Retrospective
- Compare the planned story points with the completed, completed late, and incomplete story points for the most recent sprint. Higher planned story points might indicate that there were impediments that reduced team velocity. For completed late story points, these might indicate that work slipped to another sprint. And for incomplete work, this could indicate that work was incorrectly prioritized, or the team may have committed to more story points than it could finish.
Reporting Distribution and Frequency¶
See InnovaSystem’s Process Guidance RA for the following activities to determine which roles are included in the communication of the measurement data:
USED IN¶
SEE ALSO¶
Process Guidance Version: 10.4